Can A Carborator Be Bad Even After It Has Been Cleaned Out

Home, Car Repair Library, Auto Parts, Accessories, Tools, Manuals & Books, Auto BLOG, Links, Index

How to Diagnose and Repair Carburetor Problems
past Larry Carley copyright 2022 AA1Car.comA carburetor uses intake vacuum to supply fuel to the engine. Equally air is pulled down through the throat of the carburetor by intake vacuum, fuel is siphoned from the carburetor'southward fuel bowl and mixed with the incoming air to course a combustible mixture. At idle, the fuel enters the carburetor pharynx through one or pocket-sized pocket-sized idle ports just in a higher place the throttle plate. At higher engine speeds, fuel is pulled through the principal metering jets into the venturi (the narrowest role of the carburetor throat). The air/fuel mixture and then flows downward through the intake manifold and into the cylinders where information technology is burned to produce power.
Though the basic functioning of a carburetor is adequately elementary, it also relies on a number of add together-on devices for cold starting, idle control and emissions. Changes in emission regulations in the early 1980s fabricated carburetors obsolete because they were unable to meet the new emission requirements. By the mid-1980s, carburetors were history on new product vehicles, having been replaced by throttle body and multiport electronic fuel injection systems.
Carburetor Bug
When a carburetor is clean and is working properly, the engine should start hands (hot or cold), idle smoothly, and accelerate without stumbling. The engine should get normal fuel economy and emissions should be within limits for the year of the vehicle.
Issues that are often blamed on a "bad" or "dirty" carburetor include hard starting, hesitation, stalling, crude idle, flooding, idling too fast and poor fuel economy. Sometimes it is the carburetor and sometimes it is something else. Carburetors tin can be tricky to rebuilt, and expensive to replace, so you want to be sure of your diagnosis earlier y'all bear upon this critical part.

A choke is necessary for cold starting to richen the Air/Fuel mixture and increase idle speed while the engine is warming up.
Hard Cold Starting Problems
Hard starting can be caused past a choke that fails to close and causes a rich fuel mixture when the engine is cold. But at that place's no need to rebuild or replace the carburetor if all that's needed is a uncomplicated adjustment or cleaning of the choke mechanism and linkage. Chokes are very sensitive, and easily misadjusted (which is why the government required the car makers to make asphyxiate and idle mixture adjustments "tamper-resistant" in the 1980s).
Inside the choke housing is a coiled bi-metal heat-sensing spring that contracts when information technology cools and aggrandize (unwinds) when it gets hot. The spring opens and closes the choke plate on top of the carburetor. The spring is inside a black plastic choke housing on the top or side of the carburetor. The leap is heated past an electric heating chemical element inside the cover and/or oestrus from the exhaust manifold that is siphoned upward into the housing through a small metallic tube. If the heating curlicue has burned out or is non receiving voltage, or the heat riser is plugged with rust, loose or missing, the choke will not warm up properly. This volition crusade the asphyxiate to say on all the fourth dimension, or besides long, making the engine run rich and idle too fast.
If the bi-metal choke spring is broken, the asphyxiate will never shut. A cold engine needs a very rich mixture to start, so if the choke isn't working it will suck too much air. A broken choke will also prevent the engine from idling properly (no fast idle while it is warming upward) which can cause it to stall until it reaches normal operating temperature.
If the shaft that opens and closes the asphyxiate is dirty, information technology may cause the asphyxiate to stick. The same goes for the asphyxiate linkage if it is dirty or damaged.
Even if the choke is defective, a choke repair kit or a new bimetal spring should be all that'due south necessary to eliminate the starting trouble. Replacing the entire carburetor is unnecessary and is the aforementioned as replacing the engine because the water pump is bad.
Other causes of hard starting include vacuum leaks, ignition bug (worn or muddied spark plugs, bad plug wires, cap, rotor, etc.), low compression, even a weak starter or battery.
Hard Hot Starting Bug
As for hot starting problems, the carburetor is seldom to blame. A hot start status is usually the result of too much heat in the vicinity of the carburetor, fuel lines or fuel pump. Heat causes the fuel in the fuel lines, carburetor bowl or pump to boil. This creates a "vapor lock" status which can make a hot engine hard to start. Replacing or rebuilding the carburetor wouldn't solve annihilation because the real culprit is estrus. What needs to be done here is to reroute the fuel line away from sources of estrus (like the frazzle manifold and pipe), and/or to insulate the fuel line by fabricating aheat shield or wrapping the fuel line with insulation.
Hot start issues can also be caused past excessive resistance in a starter, poor battery cablevision connections, or a faulty ignition module that acts up when information technology overheats.
Hesitation or Stumble When Accelerating
Hesitation is a archetype symptom of a lean fuel mixture (too much air, non enough fuel) and can be caused by a muddy or misadjusted carburetor, or 1 with a weak accelerator pump or worn throttle shafts. Rebuilding or replacing the carburetor may be necessary.
The accelerator pump squirts and extra dose of fuel into the throat of the carburetor when the throttle opens. This helps starting time the extra gulp of air that is sucked in until fuel flow through the metering circuits can catch upwards to the change in air velocity through the venturi (the narrow part of the carburetor throat). The accelerator pump may use a rubber diaphragm or a rubber loving cup on a piston to pump fuel through its belch nozzles. If the diaphragm is torn or the piston piston seal is worn, the accelerator pump may not deliver information technology'southward normal dose of fuel. Or, if the discharge nozzles are plugged with dirt or fuel varnish deposits, information technology can restrict fuel menses.
The performance of the accelerator pump can be checked past removing the air filter, looking down into the carburetor, and pumping the throttle. You should run into a jet of fuel eject into each of the front venturis (barrels) of the carburetor. If no fuel squirts out, or the stream is very weak, or only ane of the two discharge nozzles on a two-butt or 4-barrel carburetor are working, the accelerator pump circuit has a problem.
Fuel usually enters the accelerator pump past a ane-mode steel cheque brawl. The ball lets fuel in, merely is pushed dorsum against its seat past pressure within the pump when the throttle opens. If this check brawl is stuck open, it acts similar a pressure leak and prevents the accelerator pump from squirting fuel through the discharge nozzles. If the check ball is stuck shut, it will prevent fuel from inbound the pump and there will be no fuel to pump through the discharge nozzles.
If the carburetor jets are coated with fuel varnish deposits, or at that place is clay within the fuel bowl, this can restrict the flow of fuel causing a lean status. Cleaning the carburetor with carburetor cleaner tin get rid of the dirt and varnish deposits to restore normal operation.
Air leaks elsewhere on the engine can also lean out the fuel mixture. Air can enter the intake manifold through loose or croaky vacuum hoses, emission hose or the PCV system. Vacuum leaks in the carburetor base gasket or insulator, intake manifold gaskets, power brake booster or other vacuum accessories can admit unwanted air. Air tin can fifty-fifty become into the manifold past badly worn valve guides and seals.
A lacking EGR valve that fails to close at idle or when the engine is cold tin be another cause of hesitation.
Other causes may include a defective distributor advance mechanism, a weak ignition scroll, carbon tracks on the coil tower or benefactor cap, bad plug wires, worn or muddy spark plugs that misfire when the engine is under load, or even an exhaust restriction. Fifty-fifty bad gas tin crusade hesitation problems. So earlier the carburetor is rebuilt or replaced, these other possibilities need to be investigated an ruled out.
Hesitation Nether Load
A hesitation, stumble or misfire that occurs when the engine is under load tin can be caused past a faulty power valve inside the carburetor. A carburetor uses intake vacuum to pull fuel through its metering circuits. Equally engine load increases and the throttle opens wider, intake vacuum drops. This tin reduce the flow of fuel and make the fuel mixture go lean, and so the power valve has a spring-loaded vacuum-sensing diaphragm that opens to increase fuel catamenia when vacuum drops. If the diaphragm has failed or the valve is clogged with dirt or fuel varnish deposits, it must be replaced. A new ability valve is usually included with a carburetor rebuild kit.
Hesitation or misfiring nether load can also be caused by a weak ignition whorl, or cracks in the coil or distributor cap, or bad spark plug wires.
Stalling
An engine tin stall when common cold if the fast idle speed is not set high enough. It may also stall when it has warmed upwardly if the idle speed is set too low, if the idle the fuel mixture is too lean, if the fuel is contaminated with water (or likewise much alcohol), or if the if at that place is not enough fuel pressure to keep the carburetor bowl filled. Adjusting the fast idle, regular idle speeds and/or idle mixture adjustments can frequently eliminate a hot or cold stalling trouble.

The fast idle linkage increases idle speed when the engine is cold and then information technology will not stall. Adjusting the choke for a richer setting may solve the problem.
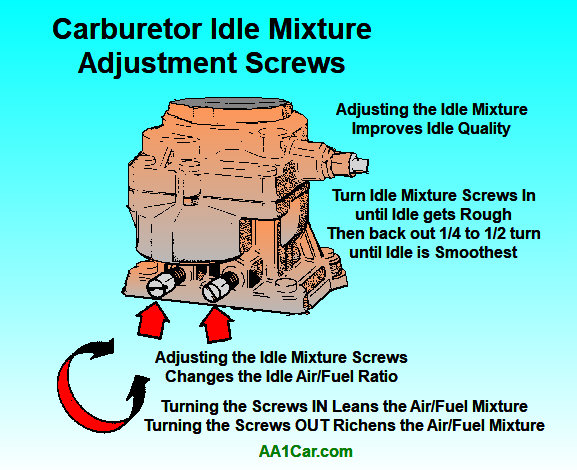
If the Idle Mixture aligning screws are adjusted too lean, the engine may stall.
Stalling can too exist caused by air and vacuum leaks in the carburetor itself (leaky gaskets and seals) betwixt the carburetor base plate and intake manifold (bad base of operations gasket), or in any of the vacuum hoses that connect to the carburetor or intake manifold. If air is existence sucked into the engine though a vacuum lea,k, information technology will lean out the Air/Fuel mixture causing a crude idle and stalling. The cure is to locate and repair the vacuum leak.
Stalling can also exist caused by a muddied carburetor. If the jets or idle circuit inside the carburetor are dirty or gummed up with fuel varnish, they won't flow enough fuel causing the Air/Fuel mixture to be too lean. Cleaning the carburetor with carburetor cleaner and/or running some Bounding main Cream or a similar solvent through the carburetor may solve the problem. If not, the carburetor may have to be disassembled for a thorough cleaning, and rebuilt with new gaskets and seals..
If adjusting, cleaning or replacing a carburetor fails to eliminate a stalling problem, the underlying cause is probable a weak fuel pump, plugged fuel filter or fuel line, or bad gas (as well much water or alcohol).
The carburetor may have to be replaced if the throttle shafts are worn and leaking air, or the carburetor housing is warped or damaged.
On vehicles with calculator-controlled idle speed, an inoperative or defective idle speed control (ISC) motor tin make an engine stall. The ISC motor controls idle speed using inputs from the engine computer. If the ISC motor is receiving voltage and is properly grounded but does not change position, the motor is burned out and needs to exist replaced. The motor may accept failed because a vacuum leak caused it to overtax itself in a vain attempt to recoup for the unwanted air.
Rough Idle
A rough idle condition is unremarkably caused by an overly lean fuel mixture that results in lean misfire. A common cause of idle problems is air leaks between the carburetor and intake manifold (tighten the carburetor base of operations bolts or supersede the gasket under the carburetor), air leaks in vacuum lines or the PCV system or EGR valve. Other carburetor-related causes include an idle mixture adjustment prepare too lean (back out the idle mixture adjustment screw one quarter of a plough at a fourth dimension until he idle quality improves), or a dirty idle mixture circuit (which may crave cleaning and rebuilding the carburetor).
Other possible causes of a rough idle include a defective charcoal canister purge control valve that is not closing and is leaking fuel vapors dorsum into the carburetor, excessive pinch blowby (worn rings or cylinders), weak or broken valve springs, or ignition misfiring due to worn or dirty spark plugs, bad plug wires or a weak ignition roll.
Idles Too Fast
This type of idle problem usually caused by the automatic choke. If the asphyxiate is sticking, the engine will stay at fast idle too long. Audit the asphyxiate and choke linkage, and clean or repair every bit needed.
There is a separate fast idle adjustment spiral on the asphyxiate linkage that controls engine speed while the engine is warming up. The tip of the screw rests against a cam that slowly rotates as the choke opens during engine warm up. Turn this spiral counterclockwise to decrease the fast idle speed, or clockwise to increase fast idle speed.
A high idle speed can also be caused by vacuum leaks that let air to enter the manifold (leaky PCV hose, ability steering booster hose or other big vacuum hose). Another crusade may be a defective ISC motor stuck in the extended (high idle speed) position.
Flooding
This is a problem that is usually (but not always) the carburetor's fault. The carburetor may inundation if clay enters the needle valve and prevents it from closing. With no way to shut off the flow of fuel, the basin overflows and spills fuel into the carburetor pharynx or out the bowl vents. A flooded engine may non start because the plugs are moisture with fuel.
Alert: Flooding tin be a very dangerous situation because it creates a serious fire hazard if fuel spills out of the carburetor onto a hot engine.
A carburetor can also flood if the float inside the fuel basin is set too high or develops a leak and sinks (this applies to hollow brass or plastic floats primarily). If all that is needed is a new float, at that place is no real need to replace the entire carburetor. Floats are not part of a rebuild kit, and so if new gaskets are also needed, a rebuild kit volition have to be purchased, as well.
Flooding can also be caused by excessive fuel pressure forcing fuel past the needle valve. Flooding may as well be caused by excessive heat in some instances. A heat riser valve on a V6 or V8 engine that sticks shut may create a hot spot nether the intake manifold that causes the fuel in the carburetor basin to boil over and flood the engine.
Poor Fuel Economy
Don't blame the carburetor if the existent problem is a lead foot on the accelerator pedal , or the engine has low compression, retarded ignition timing or an exhaust restriction (plugged converter). Just if cypher else is wrong, the carburetor may have a misadjusted or heavy bladder, or the wrong metering jets (too large).
The float setting determines the fuel level in the bowl, which in turn affects the richness of the Air/Fuel mixture. A float that is set too high or has become saturated with fuel (a problem that continues to plague many cream plastic floats today), allows the fuel level to rise and richen the fuel mixture. To diagnose this condition, the float level needs to be checked and the float weighed to determine if it has go fuel saturated. If the float is heavy, information technology needs to be replaced.
With electronic feedback carburetors, a sluggish or dead oxygen sensor can make the fuel mixture run rich. So besides tin can a lacking coolant sensor that never allows the feedback arrangement to go into airtight loop. Scanning for fault codes and checking the functioning of the feedback arrangement tin can rule out these possibilities.
If the carburetor has been replaced recently with a used carburetor or a carburetor off some other engine, the jets may not be calibrated correctly for the new awarding. Bigger jets menses more fuel and richen the fuel mixture. Installing smaller sized jets may restore the proper air/fuel mixture and good fuel economy.
One way to tell if the fuel mixture is besides rich or too lean is to examine the spark plugs. If the plugs take heavy blackness, sooty carbon deposits on the electrodes, the fuel mixture is as well rich. If the mixture is also lean, the ceramic insulator effectually the centre electrode may be xanthous or blistered in appearance. An overly lean air/fuel mixture is bad because information technology tin can crusade engine-dissentious preignition and detonation.
Should Yous Rebuild or Replace Your Carburetor
If the carburetor needs work, it tin be rebuilt with a kit or replaced with a new or remanufactured carburetor. Replacement carburetors are expensive, and may cost from $200 to $600 or more depending on the application and type of carburetor.
Cleaning and rebuilding an older one or two barrel carburetor is a relatively uncomplicated chore. A four barrel is a piffling more difficult. More complicated carburetors such as those with a variable-venturi or electronic feedback controls and tamper-resistant adjustments tin exist very difficult to rebuild, and may require the skills of an proficient. It is oftentimes easier and less risky to replace a more than complicated carburetor than to attempt a rebuild.
If the carburetor has worn throttle shafts that are leaking air, or whatsoever of the castings are cracked, warped or damaged, the carburetor cannot be rebuilt and must be replaced. The only alternative hither is if you have a 2d carburetor you can cannibalize for parts to salvage and repair the first carburetor.
Whether you are rebuilding or replacing a carburetor, you showtime demand to identify information technology. Yr, make, model and engine size may non be plenty information to find the correct carburetor kit or replacement carburetor. There is commonly a pocket-sized metal ID tag on the carburetor that volition tell the exact model number and calibration of the unit.
Fourth dimension to Upgrade to Fuel Injection?
Another option to consider if your carburetor needs to be replaced is to upgrade to an Aftermarket Fuel Injection System. It doesn't price much more than a new carburetor and yous get easier starting, smoother running and even some extra horsepower. There are various aftermarket bolt-on Throttle Torso Fuel Injection systems that are relatively like shooting fish in a barrel to install and are "cocky-tuning." They do require adding an oxygen sensor to the exhaust organization for feedback fuel mixture control, merely most do not require any special computer skills for tuning. The system "learns" the all-time settings every bit you drive and makes the necessary adjustments so you get good cold idle smoothness, great throttle response, and unremarkably ameliorate fuel economic system and performance than what you lot had before.
Of course, if you want to continue your fuel system 100 percentage original, than upgrading to an aftermarket fuel injection arrangement would non be an option.
 Holley 4160C
Holley 4160C Carburetor Rebuilding Tips
Before yous have a carburetor autonomously, discover an associates diagram in a service manual for reference. Carburetor kits may or may not include an associates diagram and instructions.
Too note where various vacuum hoses and lines connect to the carburetor. If necessary, depict a picture of the hose connections, or identify a piece of masking tape on each hose and write on the tape which hose goes where.
Lay the parts out on a clean piece of work bench, paper or metallic tray. Pay attention to how the parts came apart (especially linkages) so you can remember how to reassemble the parts when you lot put the carburetor dorsum together. Sentry out for pocket-sized steel cheque balls that tin be hands overlooked or lost.
When cleaning carburetor parts, use carburetor cleaner or a solvent that will not damage plastic and soft metal parts. Habiliment prophylactic gloves to avert peel contact with the cleaner or solvent. Follow utilize instructions for the cleaner or solvent, and use in a well ventilated area. Avoid breathing the fumes.
Check for a worn throttle shaft. The pigsty in the base casting can become worn over time, allowing air to be sucked in past the shaft. This volition lean out the fuel mixture, possible causing lean misfire, hesitation or stumbling problems. If the throttle shaft pigsty is worn, it can be fixed past removing the throttle shaft, drilling out the pigsty to oversize and installing a steel or contumely sleeve to restore normal clearances.
Another problem to watch out for is a bad bladder within the fuel bowl. If the float is brass, milkshake information technology to run into if in that location is any liquid inside. A pocket-sized hairline cleft in the seam can let fuel to seep into the float, causing it to sink and flood the engine with too much fuel. Many carburetors also accept plastic floats instead of brass. Some plastics soak up fuel over fourth dimension similar a sponge, making them too heavy. This causes the bladder to ride likewise low in the fuel bowl and flood the engine with too much fuel. The fix for a bad float or a heavy float is to replace it with a new one (f you can discover a replacement).
Carburetor Installation Tips
Clean the carburetor mounting surface on the intake manifold (do Not allow any dirt or gasket droppings to autumn down inside the manifold), and install a new base of operations gasket nether the carburetor. Never reuse the old gasket because they well-nigh always leak! Gasket sealer may be applied to the base gasket to reduce the chance of air leakage, just exercise NOT employ RTV silicone because it dissolves when exposed to gasoline.
Tighten the carburetor base mounting basics or bolts evenly so the gasket is clamped firmly in place. Practice NOT over-tighten the fasteners as doing so may warp or crevice the carburetor base of operations plate.
When reconnecting the fuel line and any other fittings (EGR, PCV) to the carburetor, be careful not to cross-thread the fittings, and do Not over-tighten every bit doing and so can strip the treads in the soft casting.
Install a new fuel filter to protect the carburetor from dirt.
Do NOT forget to reattach the throttle return spring(due south) on the throttle linkage. The terminal matter y'all desire is a runaway engine when y'all commencement information technology upward. If the springs are onetime and rusty, announced to be stretched or are weak, replace them with new springs. Also test the throttle linkage to make sure the throttle opens all the way when the gas pedal is floored, and that nothing binds or rubs against the linkage that might cause it to stick.
When installing the air cleaner, exercise Non over-tighten the nut that holds the air cleaner in identify as this can misconstrue and damage the carburetor casting.
Inspect all rubber fuel hoses and clamps. Replace any hose that is difficult, brittle, mushy, cracked or leaking. New clamps are also recommended. Worm-screw clamps are usually the best. Ring mode clamps lose tension with historic period, and tin can be permanently plain-featured if they are over-expanded during removal.
Double bank check all the fuel line, vacuum and emission hose connections, the throttle linkage and return bound, and so outset the engine. Recheck again for any leaks or other problems.
Carburetor Adjustments
Adjust the idle speed and idle mixture adjustment screws afterwards the engine reaches normal operating temperature. Prepare the idle speed to specifications (typically 600 to 650 rpm), and adjust the idle mixture screws for smoothest idle. Plough each idle mixture spiral in until the engine starts to stumble, so back it out about 1/4 to 1/2 turn. Proceed to arrange for smoothest idle.
The automated choke may have to be adjusted if the engine does not start easily. The choke should exist fully airtight on a cold engine, and open all the way once the engine warms up. Modest adjustments get a long means, and it may take several trial-and-error adjustments of the choke housing to get it right.
If the engine hesitates or stumbles when accelerating, the accelerator pump linkage or cam may require some adjustment to increase the volume of fuel squirted into the engine when the throttle opens. The accelerator pump linkage or cam commonly has several aligning settings, and then try the next college setting if it needs more than fuel.
If you are installing a performance carburetor, the principal metering jets that come up in the carburetor may or may not give you the best air/fuel mixture. The best functioning is unremarkably achieved with a slightly rich mixture. Jet sizes are usually indicated with a number stamped on the side of the jet. Installing slightly larger sized jets will flow more than fuel and richen the mixture. If the carburetor is running too rich, then switching to slightly smaller sized jets may give meliorate functioning. Replacing the main metering jets usually requires removing the top of the carburetor or the fuel bowls. Some racing carburetors accept jets that can exist replaced without disassembly.
Click Hither to Download or Print This Article.
 Related Articles:
Related Articles:
Carburetors vs EFI: Which Is All-time?Air/Fuel Ratios
Honda Keihin Carburetor Repair
Mechanical Fuel Pumps
Bad Gasoline Can Cause Functioning Problems
Bad Gas Update
Fuel Filters
Cheque Your Air Filter

Related Data & Resources Offsite:
Stop Fearing Your CarburetorCarburetor Mill (rebuild kits)
Exist certain to visit our other websites:

Auto Repair Yourself
Carley Automotive Software
OBD2HELP
Random-Misfire
Scan Tool Aid
TROUBLE-CODES
Source: https://aa1car.com/library/carburetor.htm
Posted by: johnsonbigod2001.blogspot.com

 Related Articles:
Related Articles:
0 Response to "Can A Carborator Be Bad Even After It Has Been Cleaned Out"
Post a Comment